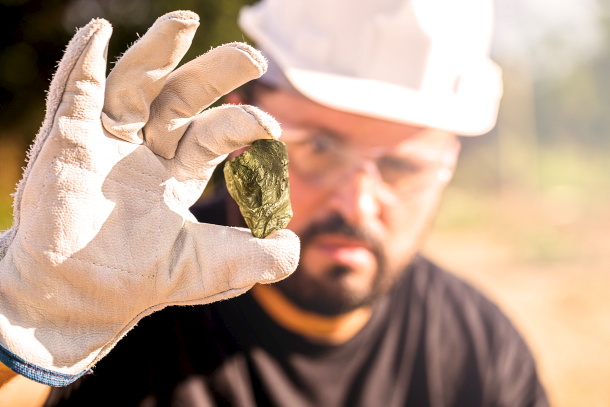
Alrosa plans to extract gold from its diamond-bearing alluvial deposits in Mirny, in Russia’s Sakha Republic.
The move comes as demand for natural diamond continues to slide, and gold prices reach record highs.
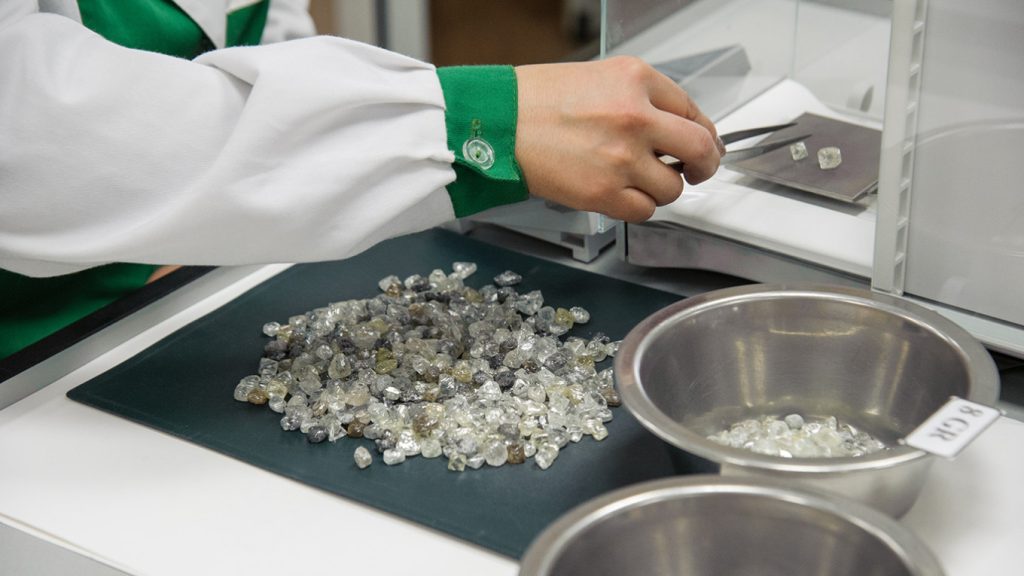
Alrosa, Russia’s state-controlled miner, announced on Friday (24 October) that it was “considering extracting gold as a byproduct during diamond mining at the Mirny-Nyurba Mining and Processing Division”.
Gold was first found in the area in 2020 and Alrosa says a team of geologists has so far recovered 433kg of it.
The proposal is that gold will be recovered as a byproduct from diamond-bearing sands and placer deposits (accumulations of valuable minerals) in the Mirny area. Alrosa will use existing processing facilities.
In 2024, the company bought the Degdekan gold deposit in the Magadan region – in a notable departure from its core activity of diamond mining.
It said it would invest over $100m in the project, which is expected to produce about 3.3 tonnes of gold annually when it reaches full capacity around 2030.
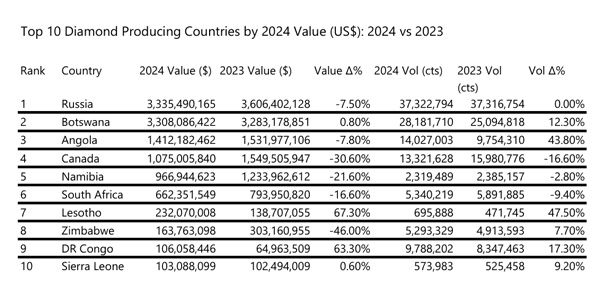
Source: DCLA