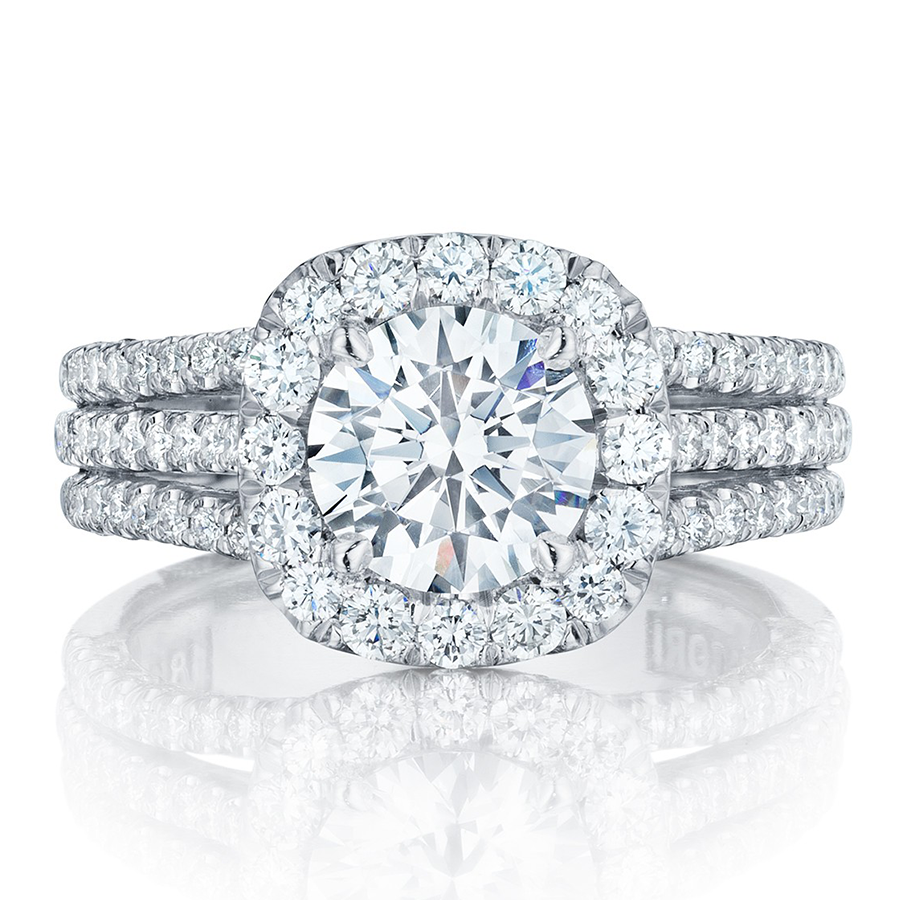
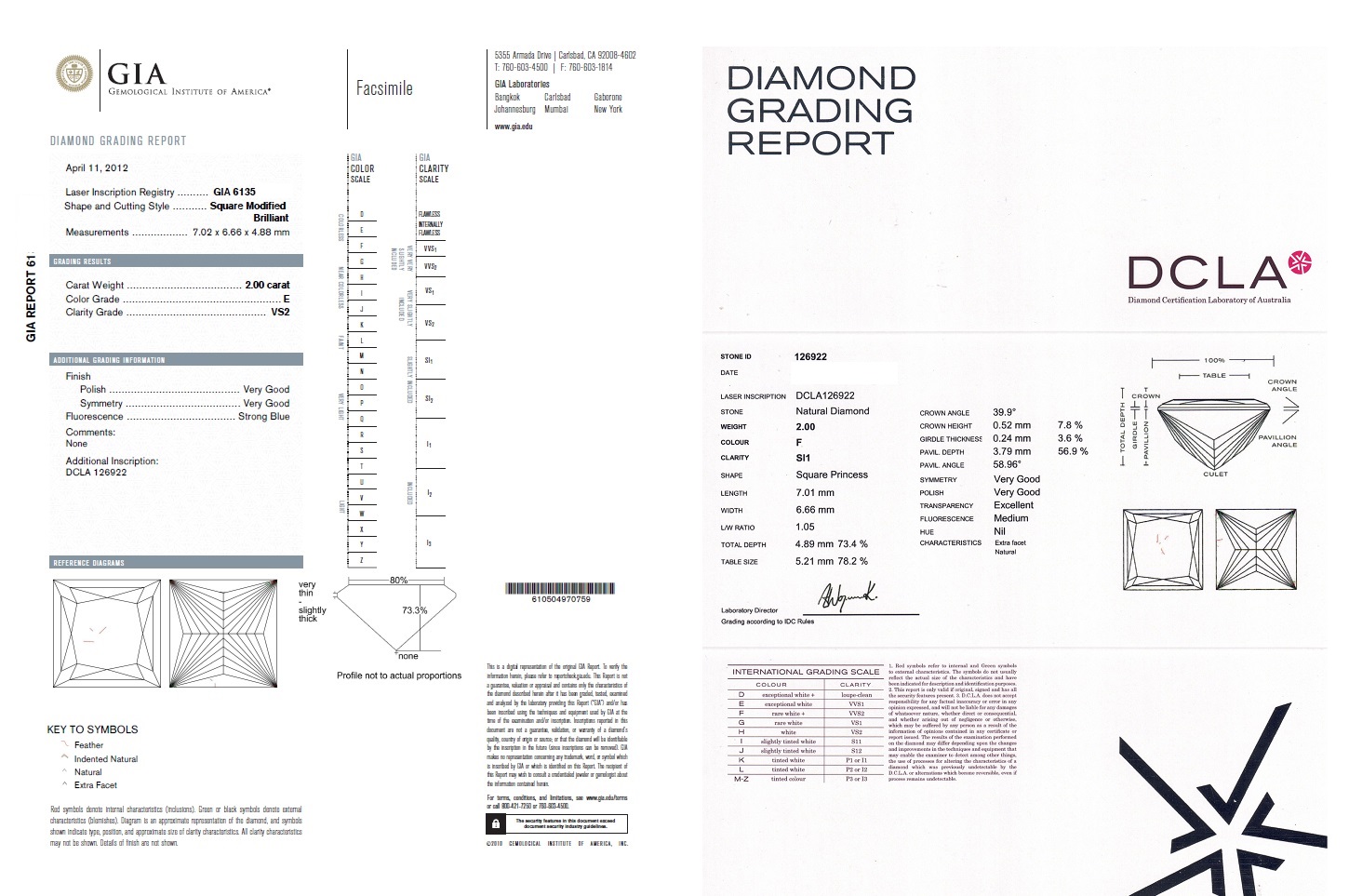
The Diamond Certification Laboratory of Australia (DCLA) reaffirms its commitment to providing precise and comprehensive grading for all diamonds, including laboratory-grown stones. This approach ensures consistency, transparency, and informed decision-making across the industry.
While the GIA has announced it will introduce a simplified classification system for lab-grown diamonds — using the categories “Premium” and “Standard” — the DCLA will maintain its tradition of detailed grading across the full range of quality characteristics. This includes reporting actual colour, clarity, cut, and carat weight for every diamond submitted, regardless of its origin.
The GIA’s new system, expected later this year, will group lab-grown diamonds based on overall appearance and finish, with certificates including carat and cut details but without specific colour and clarity grades.
DCLA recognises that both natural and laboratory-grown diamonds hold unique value and significance. By continuing to offer full grading reports, the DCLA supports both the trade and consumers in understanding and appreciating the distinct qualities of each stone.
At DCLA, we believe that consumers and the trade deserve full and detailed grading information, regardless of the diamond’s origin. Misrepresentation and confusion are more likely to arise when simplified or vague grading systems are used — especially as laboratory-grown diamonds become more prevalent in the market.
As Australia’s official CIBJO laboratory, DCLA remains dedicated to upholding the highest international standards in diamond certification and grading.